The accounts are the place where all the financial transactions of a business are contained. This template gives you everything you need to set up a simple, single-entry accounting system for your business. If your business is busy, and you find it hard to keep your books organized with this template, it may be time to consider double-entry bookkeeping. In double-entry bookkeeping, each transaction will affect at least 2 accounts.
General Ledger Example
For example, the chart of accounts I’m using has an 8-digit number range.Also, enter the company code for which you want to create the GL account. This is the most fundamental structure for collecting financial information about a business. Here you record the different types of Financial transactions and their values.

Understanding General Ledger Account
- A ledger balance is the balance in an account at the end of a business day, reflecting all the posted transactions.
- A general ledger (GL) is a comprehensive record that consolidates all of a company’s financial transactions into various accounts.
- They track a company’s value and include stockholders’ equity, common stock and retained earnings.
- Today, we use digital general ledgers, either as a standalone spreadsheet, or as part of an enterprise accounting application.
- The purpose of the general ledger book is to provide a permanent record of all financial transactions and balances classified by account.
- The accounts are the place where all the financial transactions of a business are contained.
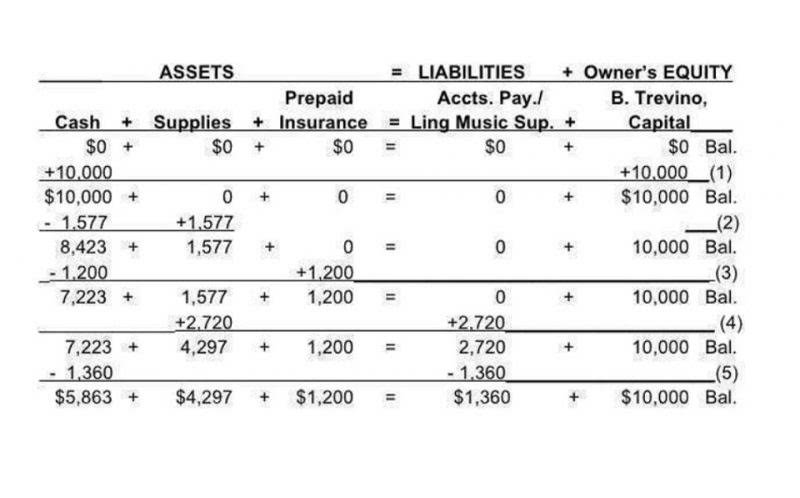
A general ledger represents the record-keeping system for a company’s financial data, with debit and credit account records validated by a trial balance. It provides a record of each financial transaction that takes place during the life of an operating company and holds account information that is needed to prepare the company’s financial statements. Transaction data is segregated by type into accounts for assets, liabilities, owners’ equity, revenues, and expenses. The general ledger is comprised of all the individual accounts needed to record the assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, expense, gain, and loss transactions of a business. In most cases, detailed transactions are recorded directly in these general ledger accounts. In the latter case, a person researching an issue in the financial statements must refer back to the subsidiary ledger to find information about the original transaction.
Income Statement

A subsidiary ledger is a ledger that contains detailed information about specific accounts included in the general ledger. It is used to keep track of transactions related to a specific group of accounts, such as accounts receivable or accounts payable. In bookkeeping, a general ledger account is used to keep track of all financial transactions that occur during a specific period. The General Ledger Account is made up of various accounts, each representing a different aspect of an organization’s financial activity.
- In double-entry bookkeeping, each transaction will affect at least 2 accounts.
- A control account operates the same as general ledger account but you record only the summarized information regarding a specific account.
- Please do not copy, reproduce, modify, distribute or disburse without express consent from Sage.These articles and related content is provided as a general guidance for informational purposes only.
- Essentially, it’s the framework for all of the financial accounts, organizing and classifying transactions.It works hand-in-hand with the GL, which actually records the transactions.
- A G/L Account (General Ledger Account) is a core element in SAP Financial Accounting (FI) used to categorize and record financial transactions.
- By consistently applying this method, you ensure the ledger remains balanced and accurate, reducing the risk of errors.
General what is a gl account ledger account reconciliation is the process to compare the general ledger with sub-ledgers and ensure consistent accuracy in records of transactions across the ledgers. The aim of general ledger reconciliation is to identify and resolve discrepancies in accounting across ledgers. In your general ledger, all transactions are organized by the account types previously listed. Not only does this give business owners the clearest possible picture of their financial status, but it also ensures they have everything they need for reporting and auditing.

What are the five main general ledger accounts?
A GL account is mapped to a financial statement version in SAP to generate financial reporting. Therefore, you can create GL accounts in SAP FI at Chart of Accounts as well as the Company Code level. By this same analogy, a ledger could be considered a folder that contains all of the notebooks or accounts in the chart of accounts. For instance, the Budgeting for Nonprofits ledger folder could have a cash notebook, accounts receivable notebook, and notes receivable notebooks in it. As discussed before, the financial entries are first recorded in a general journal. For example, goods purchased with cash will be recorded in the the general journal as a journal entry.
Where do small businesses go wrong with general ledgers?
In other words, all the GL accounts of similar categories are combined together in one account group in SAP.For example, fixed assets you can map all the cash GL accounts to the Cash account group. Similarly, you can map all the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) accounts to an Expense account group. GL account is a master data where value are stored, the value may be inventory cost or may be cost incurred for particular expenses. Just upload your form 16, claim your deductions and get your acknowledgment number online.